 Introduction: Why This Debate Matters More Than Ever
Introduction: Why This Debate Matters More Than Ever
If you’re just stepping into the world of crypto, you’ve probably stumbled across the terms centralized exchange (CEX) and decentralized exchange (DEX). These platforms serve as gateways to buying, selling, and trading cryptocurrencies. But the real question is: which is safer, more cost-effective, and potentially more profitable for beginners?
The answer isn’t as black and white as some might hope. Each has its pros and cons, and your choice could impact everything from how you manage risk to how much profit you actually walk away with. With over $1 trillion in market capitalization in 2025, the crypto world is evolving fast, and understanding the mechanics of these exchanges is crucial for any new investor.
In this post, we’ll unpack the core differences between centralized and decentralized exchanges, explore their security, fees, liquidity, user experience, and dive into which offers the better path for profitability – all while keeping things beginner-friendly.
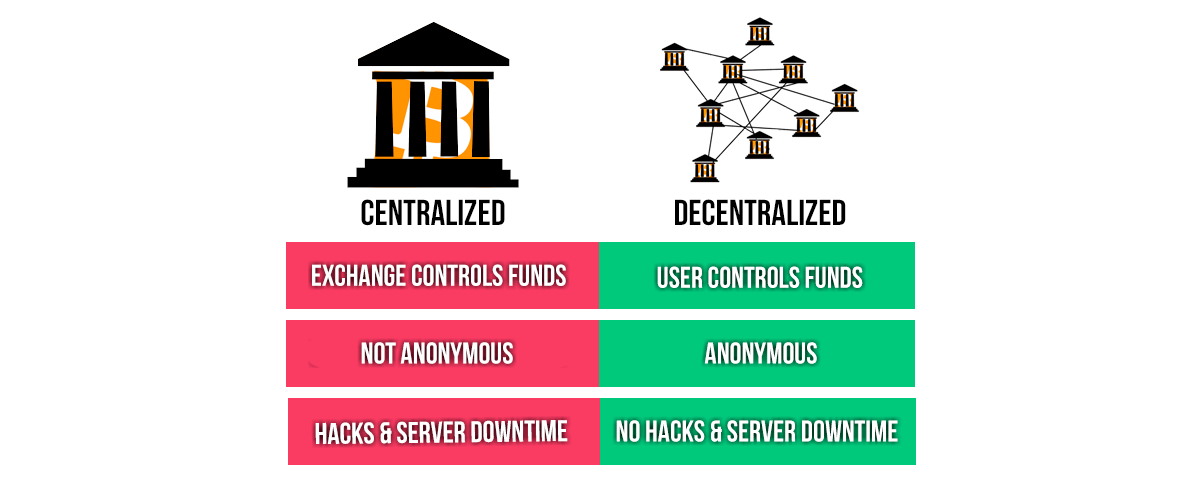
What Is a Centralized Exchange (CEX)?
A centralized exchange acts as a middleman between buyers and sellers. Think of it like a bank or stock trading platform. You trust the platform to hold your funds and execute trades on your behalf. Popular examples include Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
Key Features of CEXs:
- Custodial wallets (the platform controls your private keys)
- High liquidity and fast transaction speeds
- User-friendly interfaces and customer support
- KYC and AML compliance (you often need to verify your identity)
While centralized exchanges are convenient, they come with inherent trust-based risks and usually require handing over personal data.
What Is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
A decentralized exchange runs on blockchain technology and operates without intermediaries. You trade peer-to-peer, directly from your wallet. Platforms like Uniswap, PancakeSwap, and dYdX are well-known DEXs.
Key Features of DEXs:
- Non-custodial wallets (you control your own funds)
- No sign-ups or KYC required
- Permissionless and open-source protocols
- Trade any token listed on the platform, even obscure ones
While DEXs offer more privacy and autonomy, they can be intimidating for newcomers and less forgiving if you make a mistake.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Exchanges: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Here’s a quick snapshot of the key differences:
| Feature | Centralized Exchanges (CEX) | Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) |
|---|---|---|
| Control of Funds | Platform holds your funds | You retain full control |
| Ease of Use | Beginner-friendly UI | Often complex for newcomers |
| KYC Requirement | Yes | No |
| Security | Risk of hacking the exchange | Risk tied to smart contract bugs |
| Fees | Typically lower for high-volume traders | Often higher due to gas fees |
| Liquidity | High | Can be low, especially in newer tokens |
| Support | 24/7 customer service | Community forums, limited support |
| Token Availability | Limited to approved tokens | Wide variety including new listings |
This table shows that your choice boils down to your priorities: convenience vs. control, simplicity vs. privacy.
Is One Safer Than the Other?
CEX Security: Trust and Custody
Centralized exchanges invest heavily in cybersecurity. However, they remain prime targets for hackers. From the infamous Mt. Gox hack to more recent breaches like FTX’s collapse, history has shown that storing funds on CEXs isn’t without risk.
DEX Security: Code and Control
DEXs shift the responsibility to you. You control your wallet and keys, which eliminates custodial risk. But you must trust the code. Exploits like the Nomad bridge hack show that smart contract vulnerabilities are a real threat.
Bottom line: If you’re not comfortable managing private keys, a CEX may feel safer. But if you value autonomy and are careful with your wallet, a DEX offers more security from centralized failures.
Which Option Is Cheaper?
CEX Fees
Most centralized exchanges charge:
- Trading fees: 0.1% to 0.5% per trade
- Withdrawal fees: Fixed or network-based
- Deposit fees: Usually free with crypto, but can apply for fiat
They also offer tiered fee structures for high-volume traders or token holders (e.g., BNB holders on Binance get discounts).
DEX Fees
DEXs have a different fee model:
- Swap fees: Usually 0.3% per trade (e.g., Uniswap)
- Gas fees: Vary widely based on network congestion (especially on Ethereum)
Some DEXs on layer-2 solutions or alternative chains like Arbitrum or Polygon offer dramatically lower gas fees.
Verdict: CEXs are generally cheaper for beginners making small trades. But if you’re using a DEX on a low-fee blockchain, the cost can be competitive.
Profitability Potential: Where Can You Make More Money?
On a Centralized Exchange:
Pros:
- Easier access to fiat on/off ramps
- Margin trading and futures available
- Often better liquidity for major tokens
Cons:
- Limited selection of small-cap tokens
- CEXs can freeze accounts or restrict withdrawals
On a Decentralized Exchange:
Pros:
- Early access to new or low-cap tokens before they hit CEXs
- Participate in liquidity mining or yield farming
- No limits on trading amounts
Cons:
- Low liquidity in some tokens may cause price slippage
- High gas fees can erode profits
If you’re looking to invest in trending altcoins or experiment with DeFi opportunities, DEXs provide more profit potential. But for steady, reliable trading, CEXs may serve better.
User Experience: Convenience vs. Autonomy
One of the biggest barriers for DEX adoption among beginners is the steep learning curve.
Centralized Platforms Win on Simplicity
Platforms like Coinbase or Binance offer intuitive dashboards, mobile apps, and responsive support. You can deposit with a credit card and start trading in minutes.
Decentralized Platforms Prioritize Control
DEXs require:
- Setting up a wallet (e.g., MetaMask)
- Managing private keys and seed phrases
- Understanding slippage, gas fees, and token contracts
That said, newer DEX interfaces are becoming more user-friendly. Tools like Matcha aggregate DEX prices and simplify the experience.
Key Implications for Beginners
If you’re starting out, these are the biggest takeaways:
- CEXs are easier but involve more trust. You’re handing over your keys and personal data.
- DEXs offer privacy and control, but demand more technical competence. Mistakes (like sending funds to the wrong contract) can be irreversible.
- Security is a shared responsibility. Neither option is 100% safe. CEXs can be hacked; DEXs can be exploited.
- Costs vary. Small traders may prefer CEXs, while experienced users can save (and earn more) on DEXs using low-fee chains.
- Profit opportunities differ. CEXs are for convenience and high-volume trading; DEXs unlock DeFi and early-token exposure.
Final Thoughts: Which Should You Choose?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Your decision should align with your goals, comfort with technology, and risk tolerance.
If you value simplicity, regulation, and support, start with a centralized exchange. Once you understand how crypto works and want to explore deeper opportunities like DeFi, NFT marketplaces, and passive income strategies, decentralized exchanges offer a powerful next step.
Most experienced users use both: CEXs for convenience and fiat on-ramps, DEXs for innovation and investment diversity.
Crypto isn’t just about where you trade – it’s about how much control you want to have over your financial future.
Have you tried both types of exchanges? Which do you prefer and why? Drop a comment below and share your experience.
Want more guides like this? Subscribe to our newsletter for weekly crypto deep-dives, tips, and beginner-friendly explainers.






